
Modern packaging realities would have been unimaginable to observers studying the state of the industry decades ago. But like most progressive, demand-driven businesses the consumer packaging industry continually evolves, responding to technological advances and marketplace preferences.
Although consumer cues positively shape the direction of the contract packaging industry, technology can change the playing field altogether – leading to breakthroughs like smart packaging. As new things become possible, the fast-growing segment is poised for further expansion, fusing creativity, and technology in unique smart packaging designs. If you are involved in the consumer supply chain, smart packaging is bound to play an increasingly important role in your future.
Smart Packaging Defined
Smart packaging has been a part of the landscape for years, but each new advance raises its profile. Also known as interactive packaging, intelligent packaging, or simply active packaging, the innovative approach adds another dimension of functionality to consumer packages, enabling the containers themselves to provide information about package contents.
To capture the various types of smart packaging now in use, its definition is necessarily broad.:
In essence, smart packaging uses advanced technology or capabilities to expand functionality and/or create an interactive experience.
In some cases, the interaction occurs directly with consumers, providing tactile sensations and other valuable feedback. In other applications, smart packaging interacts with consumer electronics, enabling smartphones and other devices to pick-up data from product packaging.
The Technology Behind Smart Packaging Trends
Smart packaging offers expanded functions, beyond the traditional need to protect and transport consumer goods. In its simplest form, that translates to sounds, tactile feedback, and other sensations experienced by consumers interacting with an intelligent product container. But this is only the beginning for smart, interactive packaging, which now benefits from cutting-edge electronic technology, capable of sensing and sharing wide-ranging information.
Diverse producers and brand owners now use smart packaging to monitor and improve shipping times, maintain product freshness, and reinforce safe handling practices. And as a direct conduit to end-users, smart packaging promotes consumer convenience and supply chain transparency, increasing sales and brand loyalty for tech-forward suppliers tuned-in to these important lifestyle values.
One rapidly advancing area, “printed electronics” refers to the ability to blend advanced electronic technology with thin packaging substrates. In supply chain applications, the thin, flexible material is made smart, using printing techniques capable of incorporating thin circuitry, miniature sensors, and tiny paper-thin battery power sources. Combined with advances in smartphone capabilities, intelligent packaging presents unlimited opportunities to expand package functionality and consumer interaction within competitive retail environments.
Miniaturization and electronic printing innovations have made new things possible, but advances in related technology have also made the process less costly, opening the door to its use in high-volume applications. As a result, demand for smart packaging is poised for further growth in the coming years, potentially driving the global market to levels above $28 billion annually by 2024.
Intelligent and Active Packaging in the Marketplace
Smart packaging executes specific functions in the marketplace, benefiting diverse consumer industries. The strategies currently in use can be roughly broken into two distinct categories. Active packaging most often refers to product packaging capable of sensing and regulating a package environment.
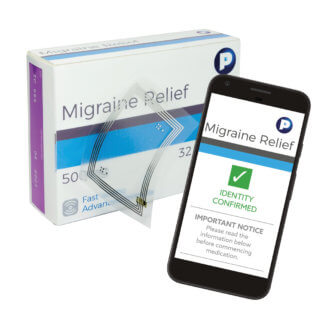
In practice, substances are deliberately added to the packaging material to enhance the shelf stability of various products, better controlling the effects of time, temperature, and other variables. Used effectively, the technology bolsters the protective function of a package, resulting in better handling conditions and product integrity. Oxygen scavengers, antimicrobial agents, and various specialized barriers are examples of active packaging technology commonly used in food-related applications.
The smart packaging subset often referred to as intelligent packaging, emphasizes the communication function of a package. Intelligent packaging sends messages to supply chain stakeholders and interacts directly with consumers and their devices. The growing use of technology responds to shifting buyer expectations, which now calls-upon savvy marketers to inform and interact with each consumer on a personal level. Applied correctly, intelligent packaging can:
- Streamline supply-chain management
- Assist product authentication with anti-counterfeit technology
- Monitor pathology within a package
- Share marketing and branding information
Smart Packaging Moves Forward
Cost-efficiency and consumer preferences drive packaging trends, so affordable smart packaging alternatives are changing the playing field for forward-looking contract packagers. In search of supply chain integrity and transparency, it appears consumers are willing to pay extra for packaging, reflecting their lifestyle values. So as high-volume smart packaging solutions have become more affordable, use of the intelligent designs has taken hold in pharma, automotive, health and beauty, and other specialized segments. As innovation tests new frontiers, cost-effective interactive packages are replacing standard options across the entire food supply chain. Examples include:
- Milk containers equipped with special carton liners designed to extend the shelf life of perishable contents
- Meat packaging labeled with smart technology, including color-changing labels indicating the contents is beyond their expiration date.
- Produce packaging capable of reducing food odors
- Specialty marketing, such as a recent campaign incorporating LEDs into consumer beverage bottles
- Time-temperature sensors furnishing feedback about perishable deliveries
- Antimicrobial packaging used to inhibit germ growth and spoilage
- Coded packages equipped to interact with smartphones, sharing anti-counterfeit protection, marketing messages, and direct consumer engagement
Although price competition may slow the rise of smart packaging in some consumer segments, the technology continues to expand into new markets. The tech-forward approach syncs with lifestyles sensitive to product and supply chain integrity, so effective brand owners use smart packages to create personal connections and stimulate brand loyalty.
As innovation and technology continue to serve-up affordable smart packaging solutions, more and more producers will benefit from gains in quality, value, and consumer confidence.

Laden with information, Well summarized. Helpful information!
Nice blog with a lot of information that enhance my knowledge. We also use smart packaging techniques and trends for our cheap custom boxes.